Theory
Years ago, a man named Pythagoras found an amazing fact about triangles:
If the triangle had a right angle (90°) ...
... and you made a square on each of the three sides, then ...
... the biggest square had the exact same area as the other two squares put together!
It is called "Pythagoraen Theorem" and can be written in one short equation:
a2 + b2 = c2
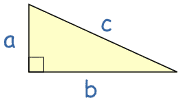
Note:
- c is the longest side of the triangle, otherwise known as the hypotenuse
- a and b are the other two sides
Definition
The longest side of the triangle is called the "hypotenuse", so the formal definition is:
In a right angled triangle:
the square of the hypotenuse is equal to
the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
But where did all this come from? Watch the video below to find out..
In other words...
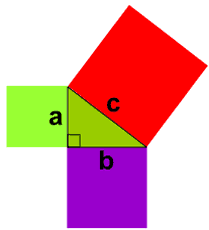
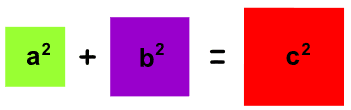
Sure ... ?
Let's see if it really works using an example.
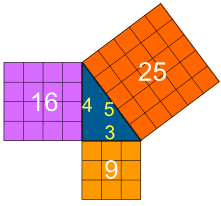
Let's check if the areas are the same:
32 + 42 = 52
Calculating this becomes:
9 + 16 = 25
It works ... like Magic!
Why Is This Useful?
If we know the lengths of two sides of a right angled triangle, we can find the length of the third side. (But remember it only works on right angled triangles!)
Check out the Examples page to see Pythagoras in action!

